Abstract
Glucosamine is one of the most widely used joint-health ingredients in dietary supplements, with global demand for glucosamine powder and bulk raw material continuing to grow. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for most adults, certain populations should avoid or use glucosamine with extreme caution. This article, written from the perspective of a 15-year dietary supplement formulation and regulatory specialist, helps glucosamine powder manufacturers and brand owners understand contraindications, potential risks, and labeling considerations to ensure consumer safety and regulatory compliance.
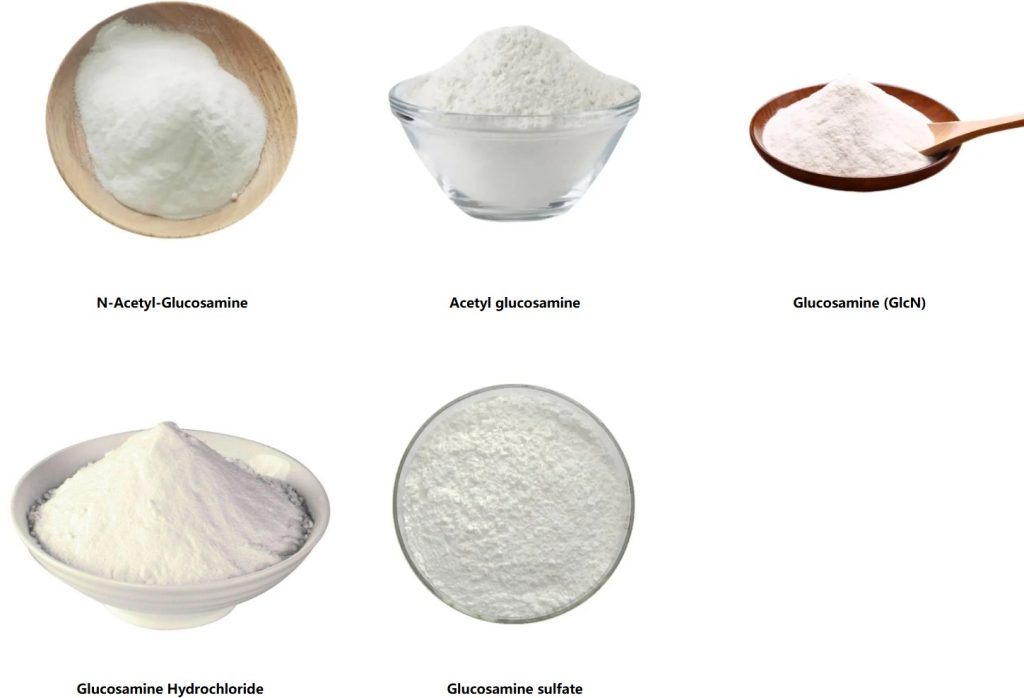
What Is Glucosamine and Why Is It So Popular in Supplements?
Glucosamine (usually supplied as glucosamine sulfate or glucosamine HCl powder) is a naturally occurring amino sugar that supports cartilage formation and synovial fluid production. Leading glucosamine manufacturers offer vegan-fermented glucosamine HCl and shellfish-derived glucosamine sulfate in bulk wholesale quantities to meet the needs of joint-health capsules, tablets, and functional beverages. Clinical studies (including the GAIT study) have shown mixed but generally positive results for mild-to-moderate osteoarthritis symptoms, driving sustained consumer demand.
Populations Who Should Completely Avoid Glucosamine
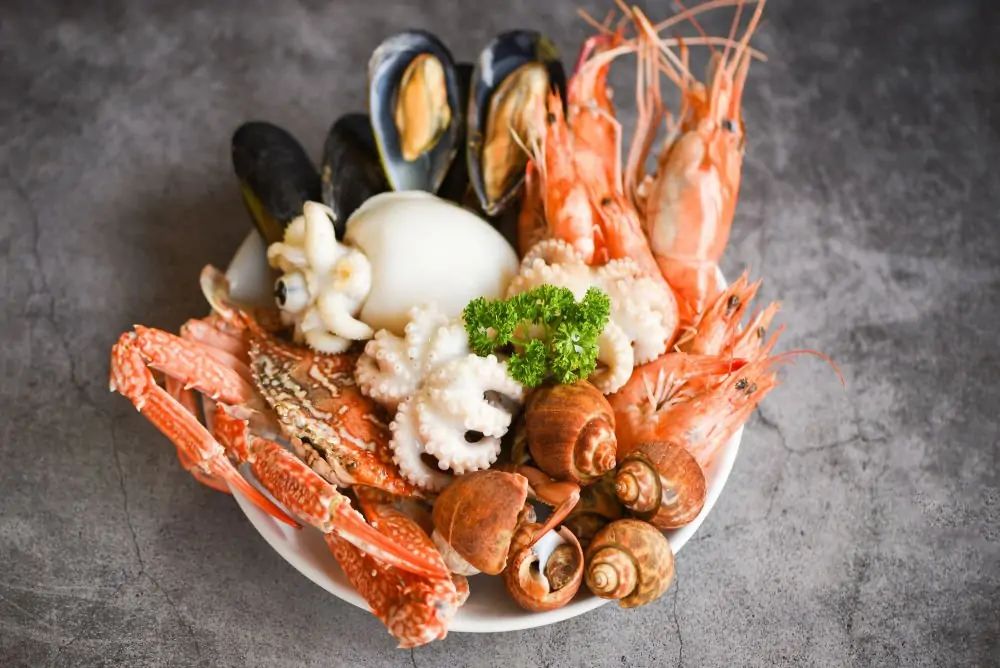
1. Individuals with Shellfish Allergy (When Using Shellfish-Derived Glucosamine)
Approximately 1–2% of adults have a shellfish allergy. Traditional glucosamine sulfate raw material is extracted from chitin in crab, shrimp, and lobster shells. Even highly purified glucosamine powder can contain trace shellfish proteins, triggering anaphylaxis in sensitive individuals. Recommendation for manufacturers: Clearly label “Contains Shellfish” or switch to vegan glucosamine HCl (fermented from corn) for allergen-free product lines.

2. People with Uncontrolled Diabetes or Glucose Intolerance
Glucosamine is an amino sugar and may theoretically affect blood glucose metabolism. Although most human studies show no significant impact on fasting glucose or HbA1c, some case reports and animal studies suggest caution. The German Commission E and several diabetes associations recommend that diabetics monitor blood sugar closely or avoid glucosamine altogether if glycemic control is poor.
3. Patients Taking Warfarin or Other Coumarin Anticoagulants
Multiple case reports and a 2017 systematic review published in Thrombosis Research documented increased INR and bleeding risk when glucosamine (especially glucosamine sulfate) is combined with warfarin. The interaction is believed to be pharmacodynamic rather than pharmacokinetic.
4. Those with Asthma (Particularly Aspirin-Sensitive Asthma)
Rare case reports link glucosamine sulfate to asthma exacerbation, possibly due to sulfite sensitivity or shellfish-derived impurities. Asthmatic patients planning to launch a glucosamine-containing product should be advised to consult their physician.
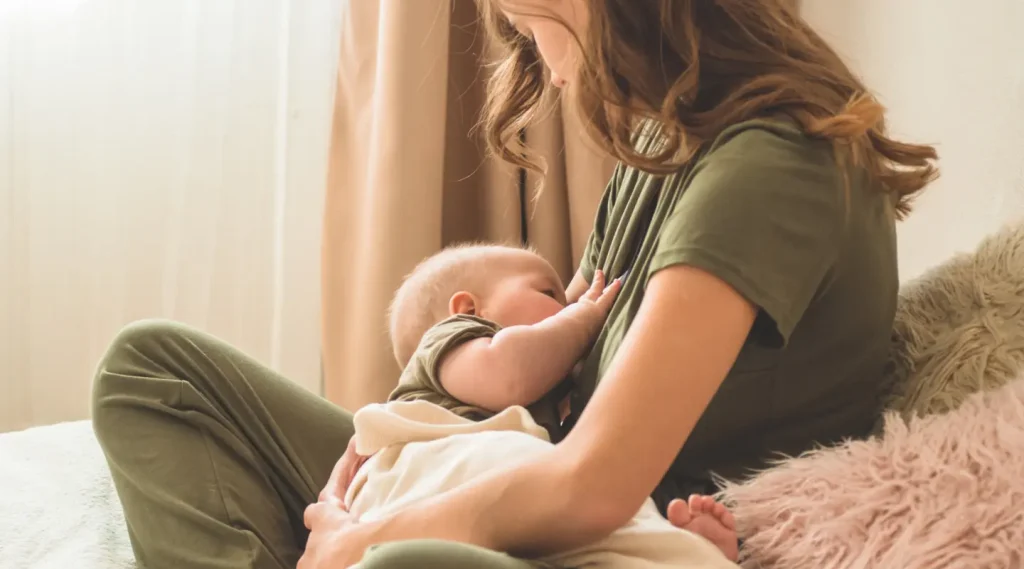

5. Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
No adequate and well-controlled studies exist in pregnant women. Glucosamine is classified as Category B in some countries, but most manufacturers and regulatory bodies (including Health Canada and Australia’s TGA) recommend avoiding it during pregnancy and lactation due to lack of safety data.
6. Children and Adolescents Under 18
Long-term safety in growing children has not been established. Pediatric rheumatologists generally do not recommend glucosamine supplements outside of clinical trials.
Moderate-Risk Groups That Require Caution and Physician Consultation
- Patients on chemotherapy (possible interaction with doxorubicin)
- Individuals with kidney disease (reduced clearance of sulfate load in glucosamine sulfate)
- People taking diuretics or anti-diabetic drugs (theoretical additive effects)
Best Practices for Glucosamine Powder Manufacturers and Formulators
- Offer both shellfish-derived and vegan glucosamine HCl vegan options in bulk wholesale to serve different market segments.
- Include clear warning statements on labels and websites: “Not suitable for individuals with shellfish allergy, pregnant or nursing women, or those taking blood-thinning medications without medical advice.”
- Recommend 1,500 mg/day dosage (the most studied dose) and advise consumers to consult healthcare providers if they belong to any risk group.
- Third-party test every batch for shellfish allergen residues (<5 ppm) when producing non-vegan glucosamine powder.
Summary
While glucosamine remains a safe and effective joint-support ingredient for the majority of adults, manufacturers have a responsibility to communicate contraindications clearly. By understanding who should avoid glucosamine — including those with shellfish allergies, uncontrolled diabetes, warfarin use, asthma, pregnancy, or pediatric status — supplement brands can minimize adverse event reports, protect consumers, and maintain trust. Offering both traditional and vegan glucosamine raw material in bulk gives formulators the flexibility to create safer, more inclusive products.
FAQ
Q: Is glucosamine safe for everyone? A: No. People with shellfish allergy, pregnant/nursing women, children, and patients on warfarin should avoid it or consult a doctor first.
Q: Can diabetics take glucosamine powder? A: Most can, but those with poor glycemic control should monitor blood sugar closely or choose alternative joint-support ingredients.
Q: Should I choose glucosamine sulfate or HCl for bulk wholesale? A: Glucosamine HCl (especially vegan) is preferred for allergen-free and vegan products. Glucosamine sulfate has slightly more clinical data for osteoarthritis.
Q: Where can I source high-quality glucosamine raw material? A: Look for GMP-certified manufacturers offering COA, third-party allergen testing, and both shellfish-derived and vegan options with competitive bulk pricing.
By proactively addressing these safety considerations, dietary supplement manufacturers can continue to meet growing demand for glucosamine powder while prioritizing consumer safety and regulatory compliance.