Glucosamine and N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) are both naturally occurring compounds derived from glucose, yet they serve different roles in the body and in nutritional applications. Understanding their distinctions helps formulators and consumers choose the right ingredient for joint health or skin-support formulations.
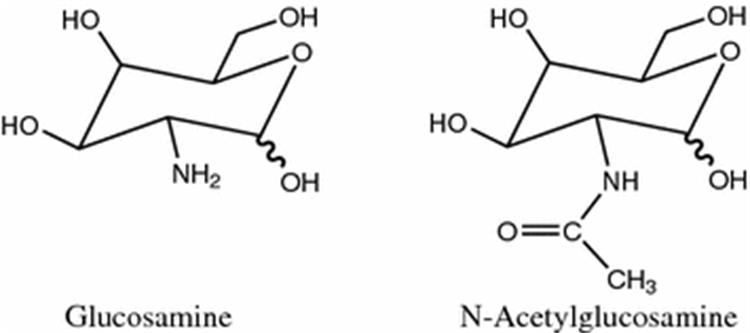
Structural Difference
Glucosamine is a simple amino sugar, often found as glucosamine sulfate or glucosamine hydrochloride. N-Acetylglucosamine, on the other hand, is a derivative of glucosamine with an added acetyl group. This small chemical change affects how each compound behaves biologically and how it is absorbed by the body.
Function and Application
Glucosamine is widely used in joint health supplements. It supports cartilage formation, lubrication, and mobility, making it a popular ingredient in sports nutrition and senior care formulations.
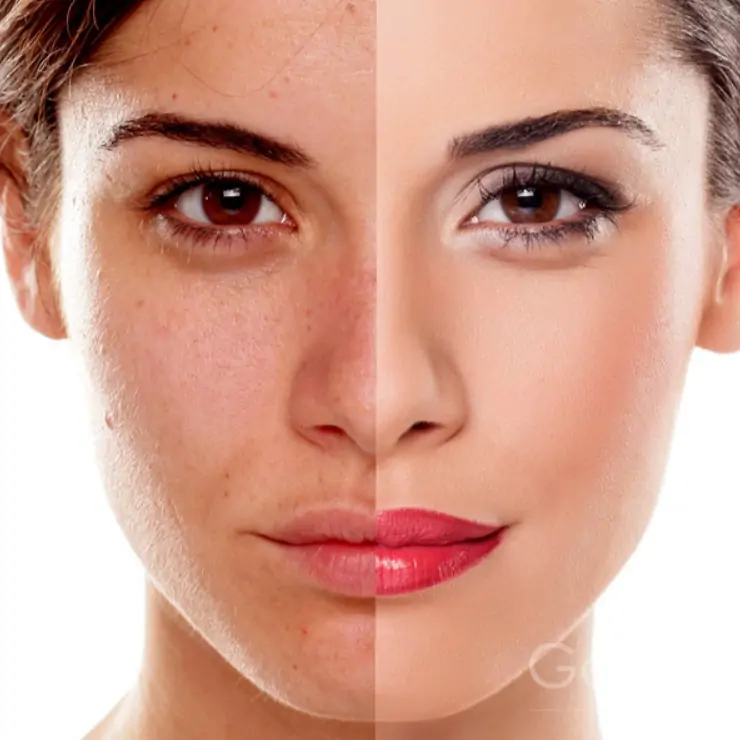
N-Acetylglucosamine is more closely related to hyaluronic acid metabolism and is often used in products that target skin hydration, intestinal health, and anti-aging applications. Its excellent solubility and gentle nature make it suitable for cosmetic and functional food formulations.

Production and Supply
Both glucosamine and N-Acetylglucosamine can be produced through shellfish or plant-based fermentation sources. As a professional powder raw material manufacturer and supplier, we offer high-purity glucosamine and N-Acetylglucosamine powders with customizable specifications to meet different formulation needs.
Conclusion
While glucosamine focuses on joint support, N-Acetylglucosamine extends its benefits to skin and digestive health. Choosing between them depends on the intended product function and formulation direction.
Reference and Disclaimer:
Information in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Functions mentioned above are supported by scientific studies, including data from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and PubChem. Always consult healthcare professionals before using dietary supplements.