Executive Summary
Recent legal settlements in the glucosamine supplements market highlight the importance of transparent marketing and quality assurance for businesses sourcing glucosamine raw material. A class action lawsuit involving a popular glucosamine product has resulted in potential cash payments for eligible New York purchasers from 2013 to 2021, underscoring the need for manufacturers to prioritize evidence-based claims and regulatory compliance. As a glucosamine manufacturer specializing in high-purity glucosamine powder and related derivatives, this article explores the compound’s role, applications, and best practices for sourcing glucosamine raw material, providing actionable insights for supplement formulators and distributors aiming to navigate this evolving landscape responsibly.
Recent Legal Updates in Glucosamine Supplements
The glucosamine supplements sector has seen increased scrutiny over product claims, as evidenced by a recent settlement in a class action lawsuit against a major brand. The case alleged deceptive advertising regarding the benefits of glucosamine supplements, leading to an agreement that offers compensation to consumers who bought the product in New York during a specified period. While the defendant denied wrongdoing, the resolution reflects broader industry trends toward greater accountability in labeling and efficacy statements. For businesses involved in glucosamine supplements, this serves as a reminder to align marketing with substantiated scientific data, reducing risks associated with consumer litigation and enhancing trust in the supply chain.
What Is Glucosamine and How Does It Function?
Glucosamine is a naturally occurring amino sugar found in the body, particularly in cartilage and synovial fluid, where it plays a key role in maintaining joint structure and function. It is commonly derived from shellfish shells or produced synthetically through fermentation processes, making it available as glucosamine powder for use in supplements. In the human body, glucosamine contributes to the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, and collagen, which are essential components of connective tissues. This makes it a popular ingredient in formulations targeting joint health, often combined with other compounds like chondroitin or MSM for synergistic effects.
From a biochemical perspective, glucosamine acts as a precursor for building blocks that support cartilage repair and reduce inflammation. Research indicates it may help modulate pathways involved in joint degradation, though individual responses can vary based on factors such as age, dosage, and underlying conditions. For supplement manufacturers, understanding these mechanisms is crucial when developing products that incorporate glucosamine raw material, ensuring formulations are optimized for bioavailability and stability.

Potential Benefits and Applications in Nutraceuticals
Glucosamine supplements are widely used to support joint mobility and comfort, particularly among aging populations or those with active lifestyles. Studies suggest it may alleviate symptoms associated with osteoarthritis by promoting cartilage integrity and reducing pain over time, with typical dosages ranging from 1,500 mg per day in divided doses. Beyond joint health, glucosamine raw material finds applications in skincare formulations for its hydrating properties and in veterinary products for animal joint support.
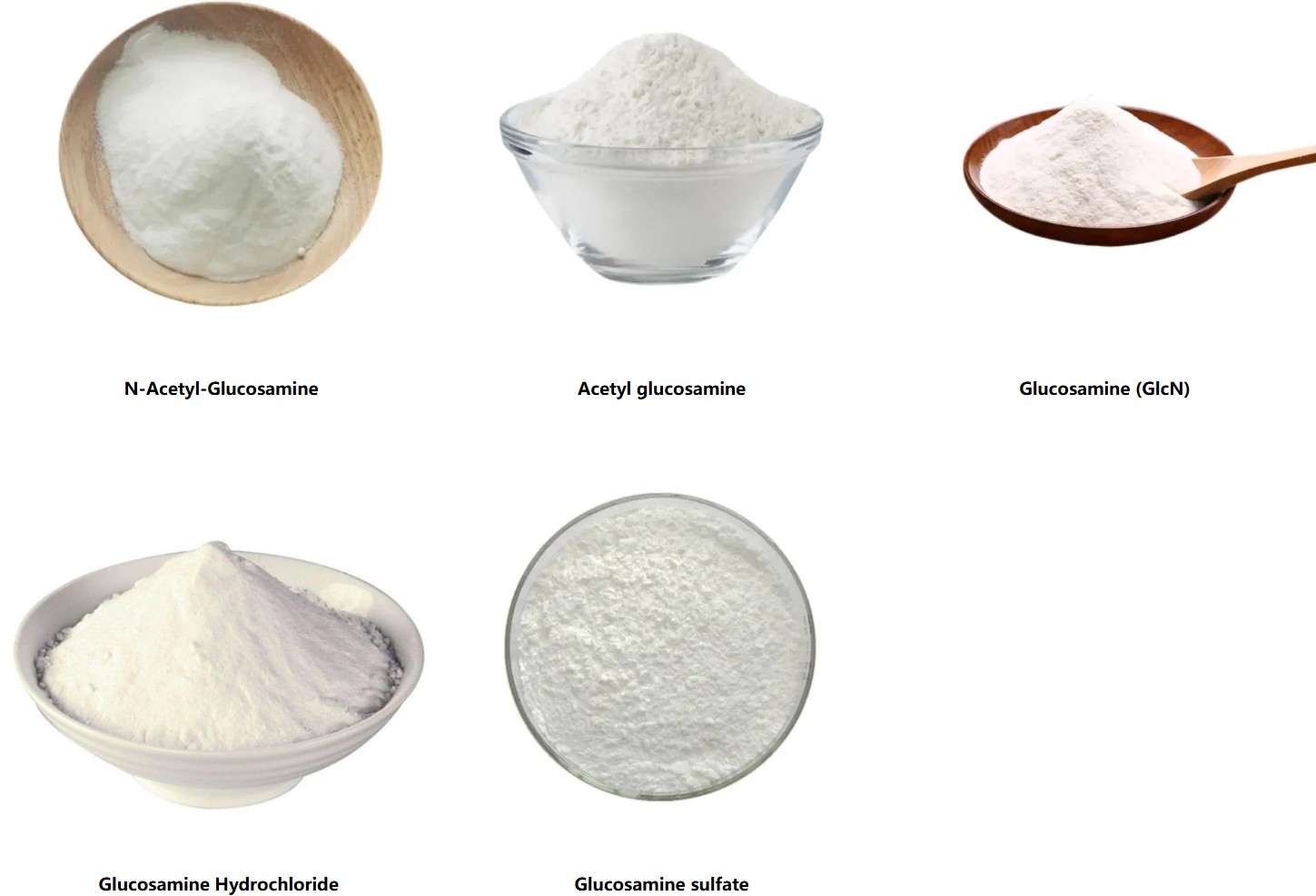
For businesses sourcing glucosamine powder, it’s important to consider variations such as glucosamine hydrochloride, sulfate, or N-acetyl-glucosamine, each offering distinct solubility and absorption profiles. Manufacturers should evaluate these based on end-product requirements, such as capsule, tablet, or liquid forms, to deliver consistent efficacy. However, benefits are not universal, and ongoing research emphasizes the need for personalized approaches rather than one-size-fits-all claims.
Best Practices for Sourcing Glucosamine Raw Material
As a glucosamine manufacturer, ensuring supply chain integrity starts with selecting high-quality glucosamine raw material that meets global standards like USP, EP, or JP pharmacopeia grades. Key considerations include purity levels (typically 98% or higher), absence of contaminants, and sustainable sourcing methods to avoid allergen concerns from shellfish-derived variants. Third-party testing for heavy metals, microbial content, and potency is essential to comply with regulations such as FDA guidelines for dietary supplements.
For supplement formulators and distributors, partnering with a reliable glucosamine manufacturer can streamline production, offering customizable options like bulk glucosamine powder with short lead times. Prioritizing traceability—from raw material extraction to final batch—helps mitigate risks and supports claims of quality. Businesses should also stay informed on market dynamics, including price fluctuations and emerging synthetic biology methods that enhance sustainability and reduce costs.

Article Summary
In summary, the glucosamine industry continues to evolve amid legal and scientific developments, emphasizing the value of transparency and evidence-based practices. By understanding glucosamine’s functions, benefits, and sourcing strategies, supplement manufacturers can create products that genuinely support end-users while minimizing regulatory hurdles. Focusing on quality glucosamine raw material from trusted sources fosters long-term business sustainability in this competitive market.
Note: Information on glucosamine’s functions and benefits is drawn from authoritative sources such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements and Mayo Clinic resources, which provide comprehensive overviews based on clinical studies.
FAQ
What are the main forms of glucosamine available as raw material? Glucosamine raw material is commonly available as glucosamine hydrochloride, glucosamine sulfate, and N-acetyl-glucosamine. Each form varies in stability and application, with hydrochloride often preferred for its high purity in glucosamine powder formulations.
How can manufacturers ensure the quality of glucosamine supplements? Quality assurance involves obtaining glucosamine raw material from certified suppliers with ISO, GMP, and third-party testing. Regular audits and batch-specific certificates of analysis help maintain standards for glucosamine supplements.
What dosage considerations apply when using glucosamine powder in products? Standard recommendations suggest 1,500 mg daily, but manufacturers should consult clinical data and regulatory bodies to tailor dosages for specific glucosamine supplements, accounting for bioavailability and user demographics.
Are there sustainability concerns with sourcing glucosamine raw material? Yes, traditional shellfish-derived glucosamine can raise environmental issues. Opting for fermented or plant-based alternatives from a reputable glucosamine manufacturer can address these while maintaining efficacy.