Abstract
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) exists in two forms: the oxidized NAD+ and the reduced NADH. The conversion of NAD+ to NADH is a fundamental redox reaction in cellular metabolism, where NAD+ accepts electrons and a hydride ion during processes like glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. This transformation enables NADH to carry energy to the electron transport chain for ATP production. As a leading NADH powder raw material manufacturer, we provide high-purity NADH raw material for bulk and wholesale applications in dietary supplements, supporting energy metabolism and overall cellular health.

What Are NAD+ and NADH?
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is an essential coenzyme found in all living cells. It acts as an electron carrier in redox reactions, alternating between its oxidized form (NAD+) and reduced form (NADH).
- NAD+ is the oxidized state, ready to accept electrons.
- NADH is the reduced state, carrying high-energy electrons and a hydrogen ion.
This cycle is critical for energy production, as NADH donates electrons to generate ATP, the cell’s primary energy currency. Maintaining optimal NAD levels supports mitochondrial function, DNA repair, and metabolic efficiency.
The Biochemical Process: How NAD+ Becomes NADH
The conversion of NAD+ to NADH occurs through a reduction reaction in catabolic pathways.
In dehydrogenase-catalyzed reactions, NAD+ accepts a hydride ion (H⁻, equivalent to two electrons and one proton) from a substrate, while a separate proton (H⁺) is released into the solution. The chemical reaction is:
NAD⁺ + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → NADH + H⁺
This primarily happens in:
- Glycolysis: In the cytosol, where glucose breakdown produces NADH.
- Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): In the mitochondria, generating multiple NADH molecules per glucose.
- Fatty Acid Oxidation: Further contributing to NADH production.
The process is reversible, allowing NADH to oxidize back to NAD+ in the electron transport chain, producing approximately 2.5-3 ATP molecules per NADH.
This efficient cycling underscores the importance of NAD in sustaining cellular energy.
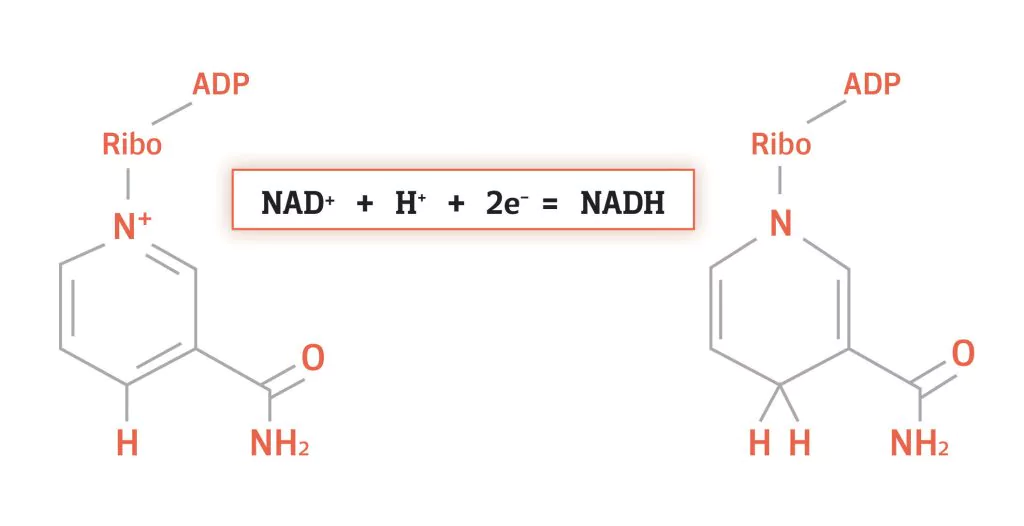
The Role of NADH in Energy Production and Health
NADH plays a pivotal role beyond energy transfer:
- It supports mitochondrial ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation.
- It contributes to antioxidant defense and cellular repair.
- Balanced NAD+/NADH ratios regulate redox homeostasis, influencing aging, metabolism, and immune function.
Research indicates that declining NAD levels with age may impair energy production, leading to fatigue and metabolic issues. Supplementing with stable forms of NADH has shown potential benefits in enhancing cellular energy, cognitive function, and stamina in preliminary studies.
As experienced manufacturers, we specialize in producing high-quality NADH powder using advanced enzymatic and stabilization techniques to ensure bioavailability and potency.
Sourcing High-Quality NADH for Supplements
For dietary supplement producers, selecting reliable NADH raw material is crucial for product efficacy. High-purity NADH powder must be stabilized to prevent degradation, often through microencapsulation with natural compounds.
Reputable NADH manufacturers offer:
- Pharmaceutical-grade purity (≥98%).
- Bulk and wholesale options for cost-effective scaling.
- Third-party testing for stability and contaminants.
Our facility produces premium NADH bulk powder, ideal for capsules, tablets, or functional foods. We provide wholesale NADH raw material with consistent quality, supporting brands in creating effective energy-boosting supplements.
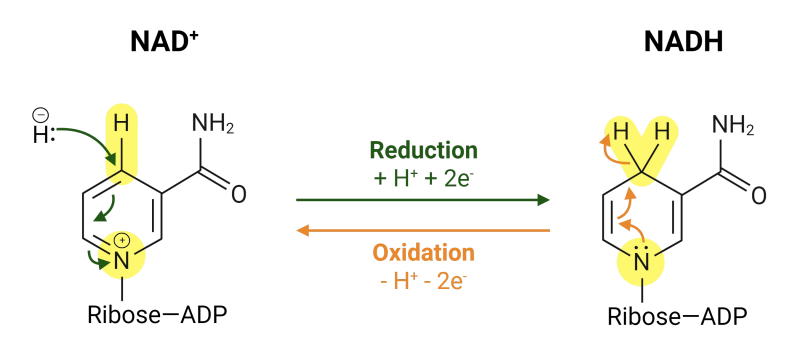
Summary
The transformation of NAD+ to NADH is a cornerstone of cellular respiration, enabling efficient energy production through electron transfer in metabolic pathways. This redox cycle not only powers ATP synthesis but also supports broader cellular functions. For supplement manufacturers seeking to harness these benefits, high-quality NADH powder from trusted sources offers a valuable ingredient. As a dedicated NADH powder manufacturer, we deliver reliable bulk and wholesale solutions to help create science-backed products that promote vitality and metabolic health.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between NAD+ and NADH? NAD+ is the oxidized form that accepts electrons to become NADH, the reduced form that donates electrons for ATP production.
2. How does the body naturally produce NADH? NADH is generated from NAD+ during glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and other metabolic processes involving dehydrogenase enzymes.
3. Can supplementing with NADH improve energy levels? Studies suggest stable NADH supplements may support cellular energy and reduce fatigue, particularly in those with low NAD levels.
4. Why choose NADH powder as a raw material for supplements? NADH powder offers high bioavailability when properly stabilized, making it ideal for bulk formulation in energy and anti-aging products.
5. Where can I source bulk NADH wholesale? Contact specialized NADH manufacturers for high-purity NADH raw material in bulk quantities, ensuring GMP compliance and third-party verification.