Abstract
NADH, the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), functions as a key electron carrier in cellular respiration. It transfers high-energy electrons from metabolic pathways such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle to the electron transport chain, supporting ATP production. This role has been extensively documented in biochemical research. Interest in NADH supplementation has grown due to its potential support for energy metabolism. High-quality, stabilized NADH powder serves as a reliable raw material for dietary supplements, available through bulk and wholesale suppliers specializing in this compound.
What Is NADH and How Does It Function in the Body?
NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced form) is a coenzyme derived from vitamin B3 (niacin) and present in all living cells. It forms a redox pair with NAD+, enabling participation in numerous enzymatic reactions.
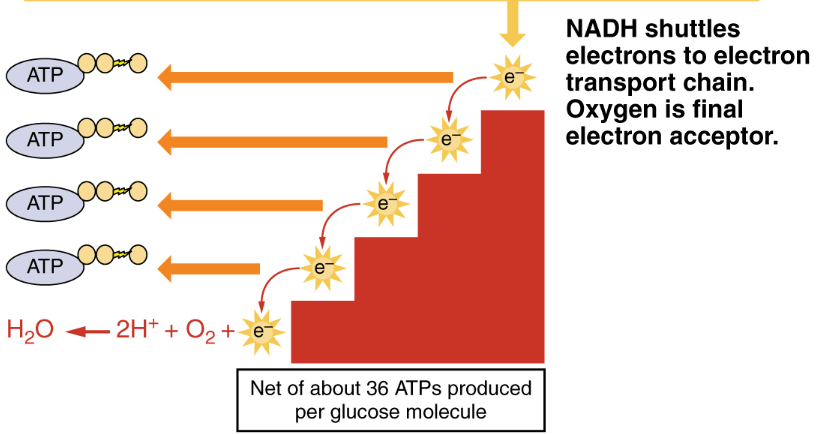
In cellular metabolism, NADH serves as an essential electron carrier. NAD+ accepts electrons during catabolic processes, becoming reduced to NADH. This NADH subsequently donates electrons to the mitochondrial electron transport chain, contributing to the proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation. Biochemical studies indicate that each NADH molecule facilitates the production of approximately 2.5 ATP molecules.
Adequate NADH/NAD+ cycling is critical for efficient energy production and overall cellular function.
Is NADH Truly an Electron Carrier? The Scientific Evidence
NADH is recognized as a primary electron carrier in aerobic metabolism. It accepts a hydride ion (equivalent to two electrons and one proton) during substrate oxidation and releases these electrons at Complex I of the electron transport chain.
Supporting evidence includes:
- Its central role in redox reactions within glycolysis, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, and the citric acid cycle.
- Electron donation leading to proton pumping and ATP generation.
- Comparative efficiency with FADH₂, where NADH typically yields higher ATP due to its entry point in the chain.
Authoritative sources, including textbooks like Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry and peer-reviewed articles from PubMed/NCBI, consistently classify NADH as a major electron carrier essential for energy transduction in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Potential Benefits of NADH Supplementation
Natural NADH levels may decline with age, oxidative stress, or increased metabolic demands. Supplementation with stabilized NADH has been explored for:
- Supporting mitochondrial function and ATP production.
- Potential benefits in energy metabolism and fatigue management, as indicated by clinical studies on conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome.
Stabilized forms of NADH powder are commonly used to maintain bioavailability, allowing effective incorporation into capsules, tablets, or powders.
Considerations for Sourcing NADH Powder as a Raw Material
NADH is a sensitive molecule susceptible to degradation by moisture, oxygen, light, and pH changes. Advanced stabilization techniques, such as microencapsulation, are employed to produce stable NADH powder suitable for supplement manufacturing.
For bulk and wholesale applications, high-purity NADH raw material (typically ≥98%) with third-party testing ensures consistency and compliance with GMP standards. Reliable manufacturers provide documentation on stability, purity, and bioavailability, supporting the development of evidence-based dietary supplements.
Article Summary
NADH functions as a vital electron carrier in cellular respiration, shuttling electrons to generate ATP—a process fundamental to energy production. Scientific literature solidly supports this role. As research into metabolic health advances, stabilized NADH powder from qualified bulk suppliers offers a practical raw material for formulating supplements aimed at supporting energy metabolism.
FAQ
1. Is NADH an electron carrier? Yes, NADH is a primary electron carrier that transfers electrons from metabolic pathways to the electron transport chain, facilitating ATP synthesis.
2. What distinguishes NAD+ from NADH? NAD+ is the oxidized form that accepts electrons to become NADH; NADH donates electrons, regenerating NAD+ in an ongoing redox cycle.
3. Are there potential benefits to NADH supplementation? Studies suggest stabilized NADH may support cellular energy production and mitochondrial health, with applications explored in fatigue-related research.
4. Why is stabilized NADH powder preferred for supplements? Pure NADH is unstable; stabilization enhances shelf life and bioavailability, making NADH powder a practical raw material for reliable formulations.
5. How is high-quality NADH raw material sourced in bulk? Bulk NADH powder is available from specialized manufacturers offering high purity, stability testing, and wholesale supply for supplement production.
6. What purity levels are typical for NADH powder used in supplements? Reputable sources provide NADH powder with purity ≥98%, verified through independent analysis to ensure efficacy and safety.