When people search for “is NAD safe”, they are often curious about whether this coenzyme, widely linked to energy and anti-aging research, is suitable for long-term use. NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) plays a critical role in cellular metabolism, but is it safe to take as a supplement?
Understanding NAD and Its Role
NAD is an essential coenzyme found in every cell of the human body. It supports energy production in mitochondria, helps repair DNA, and regulates key cellular functions. As we age, natural NAD levels decline, which is one reason why supplementation has become a focus in health and wellness industries.
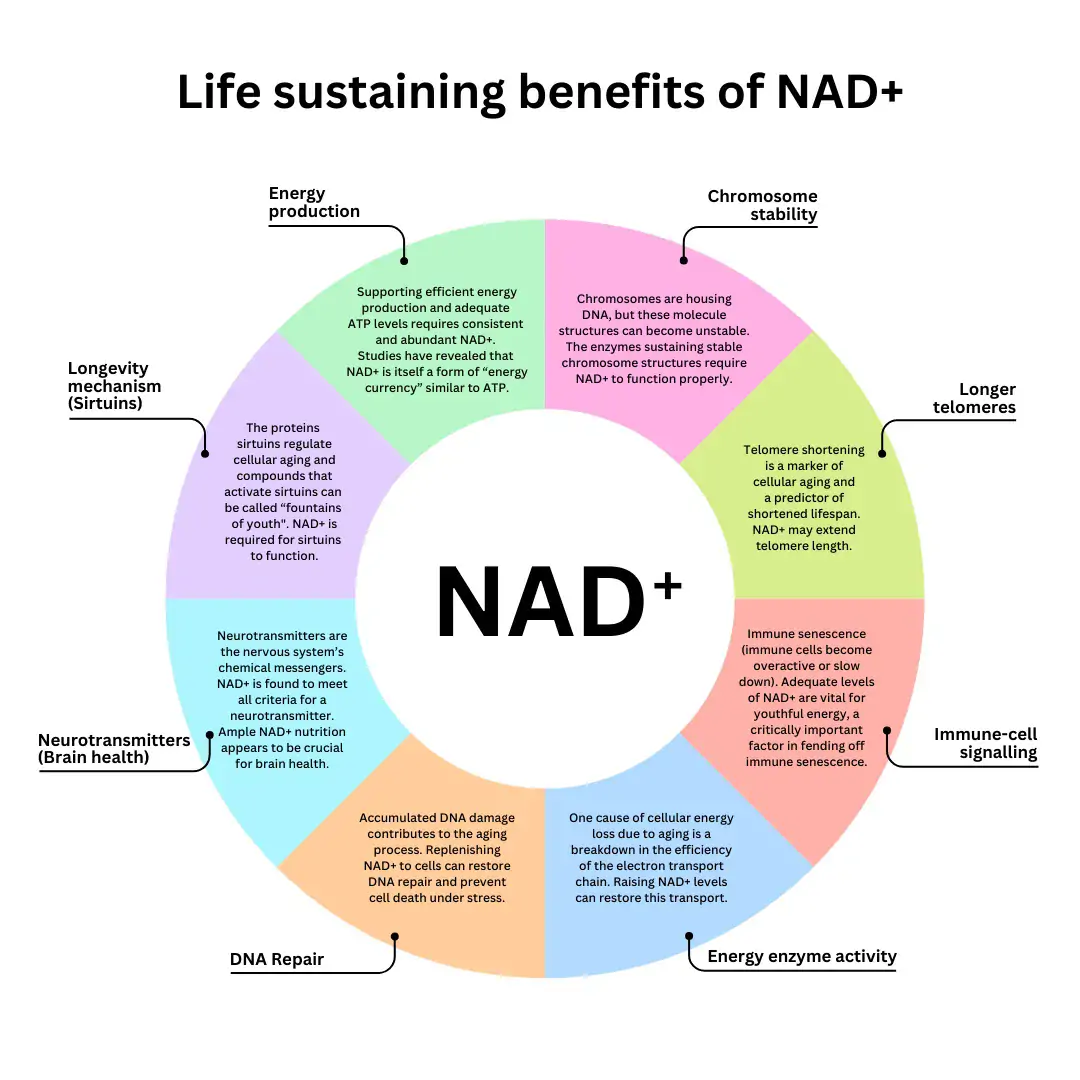
Safety Considerations of NAD
Current scientific evidence suggests that NAD and its precursors (such as NMN and NR) are generally safe for healthy adults when consumed in appropriate amounts. Studies have shown that supplementation can improve energy metabolism, support brain health, and promote healthy aging without significant adverse effects. However, like any supplement, dosage and individual health conditions matter. Consulting with a healthcare professional before long-term use is always recommended.

Why NAD Supplements Are Gaining Popularity
Because of its potential roles in supporting anti-aging, cellular repair, and metabolic health, NAD has gained strong attention in the nutraceutical and pharmaceutical markets. From athletes seeking performance recovery to wellness brands focusing on longevity, NAD-related products are becoming mainstream worldwide.
Our Role as a Reliable NAD Supplier
As interest continues to grow, the demand for high-quality NAD raw material also increases. We are a professional NAD manufacturer and bulk supplier in China, offering wholesale, customized solutions, and raw ingredient supply for global partners. Our production adheres to strict quality standards, ensuring stable and safe raw materials for your formulations.
Reference:
-
Harvard Medical School. “NAD and its role in metabolism and aging.”
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI): Research on NAD+ metabolism and safety.