Abstract
Glucosamine is a popular dietary supplement widely used to support joint health, particularly for managing symptoms of osteoarthritis. The most commonly recommended daily dosage is 1,500 mg, often in the form of glucosamine sulfate, based on extensive clinical research. This article explores evidence-based recommendations on how much glucosamine per day is appropriate, factors influencing dosage, potential benefits, safety considerations, and tips for sourcing high-quality glucosamine powder or raw materials. As a leading glucosamine powder manufacturer, we emphasize the importance of purity and bioavailability when selecting supplements for optimal results.

What Is Glucosamine and Why Is It Used?
Glucosamine is a natural compound found in the body, primarily in cartilage and synovial fluid, where it plays a key role in building and maintaining healthy joints. It is commonly supplemented to help alleviate joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
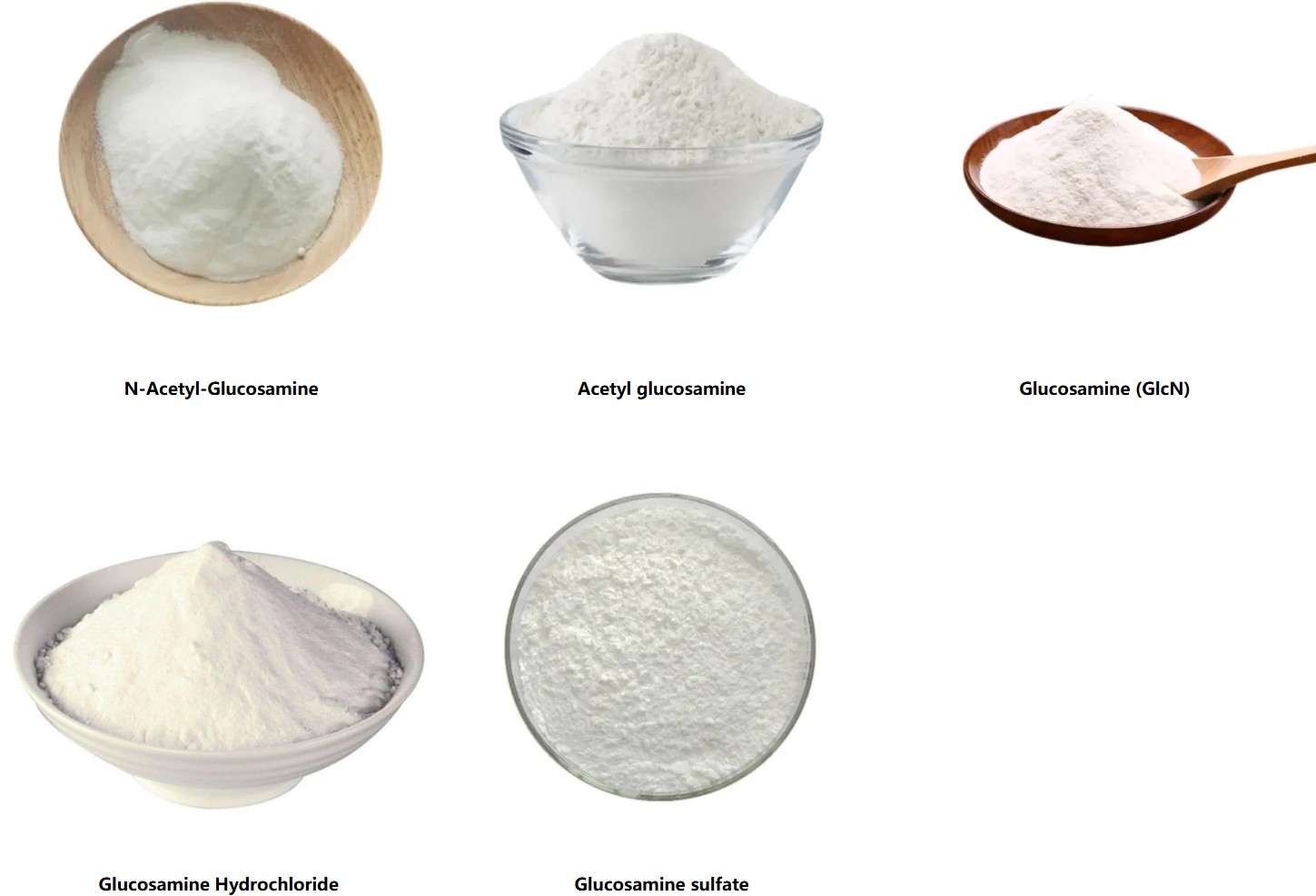
There are different forms available, including glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride. Research, including studies reviewed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and published in journals like The Lancet, indicates that glucosamine sulfate at 1,500 mg per day may reduce pain and improve function in knee osteoarthritis more effectively than placebo. While results vary across studies, glucosamine is often combined with chondroitin for enhanced benefits.
For dietary supplement manufacturers and brands seeking reliable sources, high-purity glucosamine powder is essential to ensure consistent efficacy in finished products.
Recommended Daily Dosage: How Much Glucosamine Per Day?
The standard recommended dosage for glucosamine is 1,500 mg per day, supported by multiple large-scale clinical trials such as the Glucosamine/Chondroitin Arthritis Intervention Trial (GAIT) and long-term studies showing reduced joint space narrowing.
- Typical dosing: 1,500 mg once daily or divided into three 500 mg doses.
- Form matters: Glucosamine sulfate has shown stronger evidence for symptom relief and potential structure-modifying effects compared to hydrochloride in some reviews.
- Duration: Benefits may appear after 4–8 weeks, with studies supporting use for up to 3 years.
Higher doses (up to 3,000 mg) have been explored in some research for athletes or severe cases, but 1,500 mg remains the most studied and recommended for general joint support. Always consult a healthcare provider to tailor dosage to individual needs, body weight, or specific conditions.
Factors That Influence Glucosamine Dosage
Several factors can affect how much glucosamine per day is optimal:
- Body weight: Some experts suggest adjusting for heavier individuals (e.g., up to 2,000 mg for those over 190 lbs).
- Severity of symptoms: Moderate to severe osteoarthritis may benefit more from the standard 1,500 mg dose combined with chondroitin (1,200 mg).
- Form and quality: Bioavailability varies; pharmaceutical-grade glucosamine sulfate often outperforms lower-purity options.
As a professional glucosamine raw material manufacturer, we supply bulk glucosamine powder with high purity levels to ensure supplement brands can formulate products that deliver reliable absorption and results. Wholesale options are available for businesses looking to develop effective joint health formulas.

Benefits of the Recommended Glucosamine Dosage
At 1,500 mg per day, glucosamine has been linked to:
- Reduced pain and improved mobility in osteoarthritis patients (evidence from meta-analyses and NIH-sponsored trials).
- Potential slowing of cartilage breakdown, as seen in 3-year studies where joint space narrowing was minimized.
- Mild anti-inflammatory effects, lowering markers like C-reactive protein.
These benefits make glucosamine a valuable ingredient for dietary supplements targeting active adults, aging populations, and those with joint concerns.
Safety and Side Effects of Glucosamine
Glucosamine is generally well-tolerated at recommended doses. Mild side effects may include nausea, heartburn, diarrhea, or bloating, often resolved by taking with food. It is considered safe for long-term use up to 3 years, with no significant adverse events in most trials.
Precautions:
- Shellfish allergy: Many sources derive from shellfish; vegetarian options exist.
- Interactions: May enhance effects of blood thinners like warfarin.
- Special populations: Consult a doctor if pregnant, breastfeeding, or managing diabetes.
High-quality glucosamine powder from reputable manufacturers minimizes risks of impurities.

Sourcing High-Quality Glucosamine for Supplements
For supplement brands, the quality of glucosamine raw material directly impacts product efficacy. Look for manufacturers offering:
- Pure glucosamine powder (sulfate or hydrochloride).
- Bulk and wholesale supply with third-party testing for potency and purity.
- Compliance with GMP standards to ensure safety and consistency.
Partnering with an experienced glucosamine manufacturer allows for custom formulations that meet consumer demands for effective joint support products.
Summary
Determining how much glucosamine per day—typically 1,500 mg of glucosamine sulfate—can significantly support joint health when based on scientific evidence. While individual responses vary, consistent use of high-quality supplements may help manage osteoarthritis symptoms and promote long-term mobility. For dietary supplement businesses, sourcing premium glucosamine powder in bulk from a trusted manufacturer ensures your products deliver real value to customers seeking natural joint relief.
FAQ
1. How much glucosamine per day is recommended for joint health? The most evidence-based dosage is 1,500 mg daily, often as glucosamine sulfate, taken once or in divided doses.
2. Is glucosamine sulfate or hydrochloride better? Glucosamine sulfate has more robust clinical support for osteoarthritis relief, though both forms are used effectively.
3. Can I take more than 1,500 mg of glucosamine per day? Doses up to 3,000 mg have been studied safely in some cases, but consult a healthcare provider, as higher amounts may increase mild side effects.
4. How long does it take for glucosamine to work? Benefits may start in 4–8 weeks, with optimal results often seen after 2–3 months of consistent use.
5. Where can supplement brands source high-quality glucosamine powder? Reliable manufacturers offer bulk glucosamine raw material and wholesale options with verified purity for formulating effective products.
6. Is glucosamine safe for everyone? Generally yes at recommended doses, but those with shellfish allergies, on blood thinners, or with certain conditions should seek medical advice.