Abstract
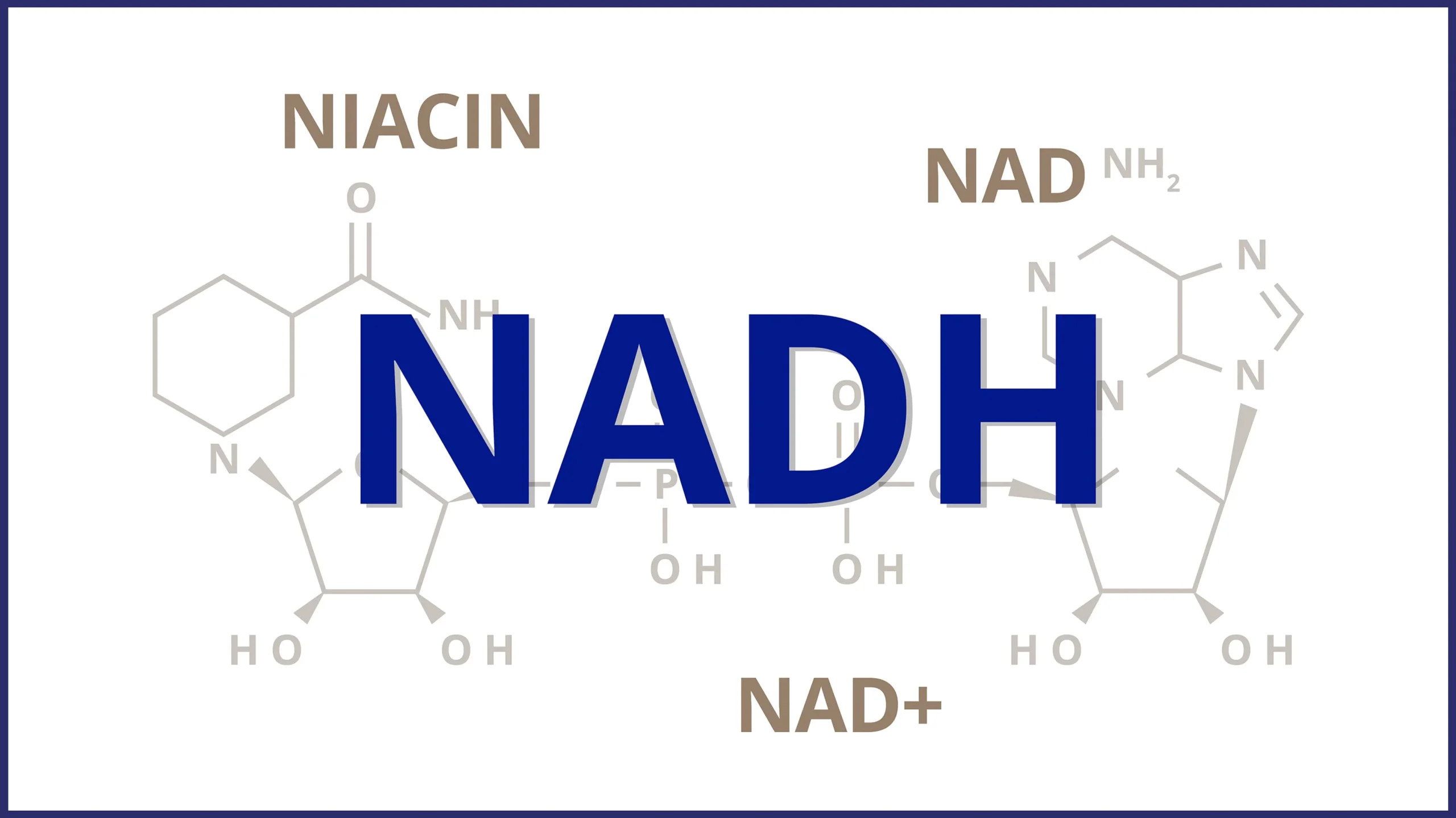
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) is a critical coenzyme involved in cellular energy production, particularly in glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration. While NADH is produced during glycolysis, high levels of NADH do not directly inhibit the pathway through allosteric mechanisms. Instead, NADH indirectly regulates glycolysis by limiting the availability of its oxidized form, NAD+, which is required for the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) step. When NAD+ is depleted due to accumulated NADH, glycolysis slows to prevent further buildup. This feedback helps maintain cellular redox balance and directs energy production toward efficient mitochondrial pathways. As a leading NADH powder manufacturer, we provide high-purity NADH raw material for bulk and wholesale applications in dietary supplements, supporting research into cellular energy and healthy aging.

What Is NADH and How Is It Produced in Glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the initial stage of glucose breakdown, occurring in the cytoplasm and yielding two pyruvate molecules, two ATP, and two NADH per glucose molecule. NADH, the reduced form of NAD+, is generated specifically in the sixth step, catalyzed by GAPDH. Here, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, transferring electrons to NAD+ to form NADH.
This production of NADH is essential for energy transfer. Under aerobic conditions, NADH shuttles electrons to the mitochondria via mechanisms like the malate-aspartate shuttle, where it contributes to ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation. In anaerobic conditions, NADH is regenerated to NAD+ via fermentation, allowing glycolysis to continue.
As an experienced NADH raw material manufacturer, we specialize in producing stable, high-quality NADH powder suitable for bulk formulations. Our NADH powder supports supplement developers in creating products that enhance cellular NAD+ recycling and energy metabolism.
Does NADH Directly Inhibit Glycolysis?
No, NADH does not act as a direct allosteric inhibitor of glycolytic enzymes, unlike ATP, which inhibits phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) and pyruvate kinase. Primary regulation of glycolysis occurs at committed steps involving hexokinase, PFK-1, and pyruvate kinase, influenced by energy status indicators like ATP, citrate, and fructose-2,6-bisphosphate.
However, high NADH levels indirectly inhibit glycolysis. The GAPDH reaction requires NAD+ as a substrate. When NADH accumulates (e.g., during hypoxia or mitochondrial dysfunction), NAD+ regeneration slows, reducing availability for GAPDH. This halts the payoff phase of glycolysis, preventing further NADH production and maintaining redox homeostasis.
Biochemical evidence from sources like NCBI and peer-reviewed studies confirms that NAD+ depletion, rather than NADH itself, limits glycolytic flux. This mechanism signals high energy availability or reduced oxidative capacity, shifting metabolism accordingly.
The Broader Role of NADH in Cellular Energy Regulation
NADH plays a pivotal role beyond glycolysis. In mitochondria, it donates electrons to the electron transport chain, driving proton pumping and ATP production—yielding up to 2.5 ATP per NADH. Maintaining an optimal NAD+/NADH ratio is crucial for metabolic flexibility.
Age-related declines in NAD+ levels impair mitochondrial function, increase oxidative stress, and contribute to fatigue and metabolic disorders. Clinical studies, including those on PubMed, show that NADH supplementation supports energy production, reduces perceived fatigue in conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome, and improves quality of life.
For supplement manufacturers seeking reliable sources, our NADH powder offers pharmaceutical-grade purity for wholesale and bulk orders. Sourced through advanced enzymatic processes, it serves as a premium NADH raw material for capsules, tablets, and functional foods targeting energy support and anti-aging.
Benefits of High-Quality NADH Supplementation
Emerging research highlights NADH’s potential in dietary supplements:
- Enhances mitochondrial ATP production and redox balance.
- Supports cognitive function and reduces fatigue, as seen in trials combining NADH with CoQ10.
- Promotes healthy aging by addressing NAD+ decline.
As a dedicated NADH manufacturer, we ensure our bulk NADH powder meets stringent quality standards, including stability for long-shelf-life formulations. Wholesale options allow seamless integration into evidence-based supplement lines.

Summary
NADH does not directly inhibit glycolysis but exerts indirect regulation by depleting NAD+, slowing the pathway when energy demands shift or oxidative capacity is limited. This elegant feedback preserves cellular efficiency. High-purity NADH raw material from trusted manufacturers like us enables the development of supplements that replenish cellular NAD+ pools, supporting vitality and metabolic health. For bulk NADH powder inquiries or wholesale partnerships, contact a specialized NADH manufacturer to source premium ingredients backed by science.
FAQ
1. Does NADH inhibit glycolysis directly? No. NADH indirectly slows glycolysis by reducing NAD+ availability for the GAPDH step, not through allosteric inhibition.
2. Why is NAD+ regeneration important for glycolysis? Glycolysis requires NAD+ to accept electrons in the GAPDH reaction. Without regeneration (via mitochondria or fermentation), the pathway halts.
3. What are the benefits of NADH supplements? Studies suggest NADH supports energy levels, reduces fatigue, and aids mitochondrial function, particularly in age-related decline or chronic conditions.
4. Where can I source high-quality NADH powder for supplements? Reputable NADH manufacturers offer bulk and wholesale NADH raw material with high purity and stability for dietary supplement production.
5. Is NADH safe for long-term use? Clinical evidence indicates NADH is well-tolerated, with benefits in energy metabolism when sourced from quality manufacturers. Consult professionals for personalized use.